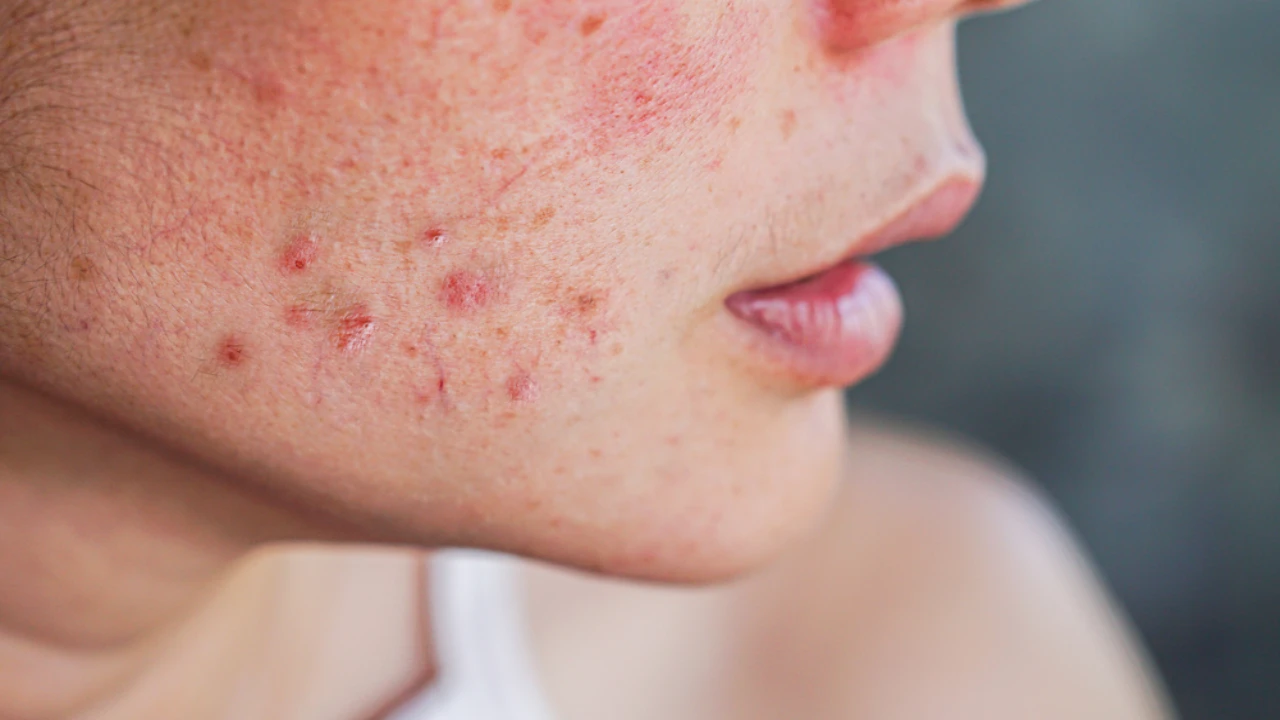
Red Spots on Skin can be concerning, especially when they appear suddenly or without an obvious cause. While they are often harmless, they can sometimes indicate underlying health issues. In this article, we’ll delve into the possible causes of red spots on the skin, their associated symptoms, and the appropriate treatment options.
Common Causes of Red Spots on the Skin:
- Petechiae: These are tiny, pinpoint red spots that occur when small blood vessels called capillaries break beneath the skin. Petechiae can be caused by various factors, including certain medications, infections, or underlying medical conditions such as thrombocytopenia (low platelet count) or vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels).
- Heat Rash: Heat rash, also known as prickly heat, occurs when sweat ducts become blocked, leading to red, itchy bumps or spots on the skin. This condition is more common in hot, humid climates or during periods of increased sweating.
- Allergic Reactions: Red spots on the skin can result from allergic reactions to foods, medications, insect bites, or contact with irritants such as certain plants or chemicals. These spots may be accompanied by itching, swelling, or other allergic symptoms.
- Rosacea: Rosacea is a chronic skin condition characterized by facial redness, flushing, and the development of small, red bumps or papules on the skin. While the exact cause of rosacea is unknown, factors such as genetics, environmental triggers, and abnormal immune responses may contribute to its development.
- Keratosis Pilaris: Keratosis pilaris is a common skin condition characterized by small, red or flesh-colored bumps that typically appear on the upper arms, thighs, buttocks, or cheeks. This condition occurs when hair follicles become clogged with keratin, a protein found in the skin.
Symptoms Associated with Red Spots on the Skin:
- Redness or discoloration of the skin
- Itching, burning, or stinging sensations
- Raised bumps, papules, or pustules
- Swelling or inflammation in the affected area
- Warmth or tenderness to the touch
Treatment Options for Red Spots on the Skin:
- Topical Treatments: Depending on the underlying cause of the red spots, topical medications such as corticosteroids, antihistamines, or antibiotics may be prescribed to reduce inflammation, itching, or bacterial infections.
- Avoidance of Triggers: If red spots are caused by allergic reactions or environmental triggers, avoiding exposure to these triggers can help prevent recurrence of symptoms. This may involve dietary changes, using hypoallergenic products, or avoiding known allergens.
- Moisturization: Keeping the skin well-hydrated with emollient creams or lotions can help alleviate symptoms of dryness, itching, or irritation associated with certain skin conditions.
- Cool Compresses: Applying cool compresses or taking cool baths can help soothe inflamed or irritated skin and provide temporary relief from itching or discomfort.
- Medical Evaluation: If red spots persist, worsen, or are accompanied by other concerning symptoms such as fever, fatigue, or unexplained bruising, it is important to seek medical evaluation to rule out underlying medical conditions and determine the appropriate course of treatment.
Comprehensive Guide to Common Skin Conditions
Skin conditions can range from minor annoyances to serious health concerns. This comprehensive guide covers some of the most common skin conditions, including heat rash, cherry angiomas, contact dermatitis, ringworm (tinea corporis), atopic dermatitis (eczema), drug rash, pityriasis rosea, blood spots (purpura), swimmer’s itch (cercarial dermatitis), psoriasis, lichen planus, petechiae, and pimples (acne vulgaris). Understanding these conditions can help in identifying symptoms, seeking appropriate treatments, and maintaining overall skin health.
Heat Rash
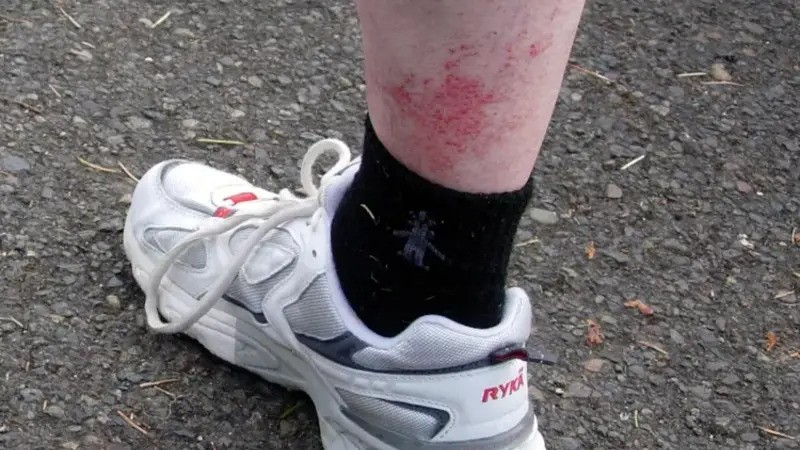

Heat rash, also known as prickly heat or miliaria, occurs when sweat is trapped in the skin, leading to inflammation and discomfort. It commonly affects people in hot, humid climates and can occur in individuals of all ages, including infants.
Symptoms
- Small red bumps: These appear on the skin, often in clusters.
- Itching or prickly sensation: The rash can cause a tingling or prickly feeling.
- Redness and mild swelling: The affected area may become red and slightly swollen.
Causes
- Blocked sweat ducts: Sweat gets trapped under the skin, causing inflammation.
- Hot and humid weather: Increases the likelihood of excessive sweating.
- Tight clothing: Can contribute to the blockage of sweat ducts.
Treatment
- Cool baths or showers: Help to soothe the skin and reduce sweating.
- Lightweight, breathable clothing: Prevents further irritation and allows the skin to breathe.
- Hydrocortisone cream: Can be used for severe itching.
- Keeping cool: Staying in an air-conditioned environment and avoiding excessive heat can help prevent the rash.
Cherry Angiomas
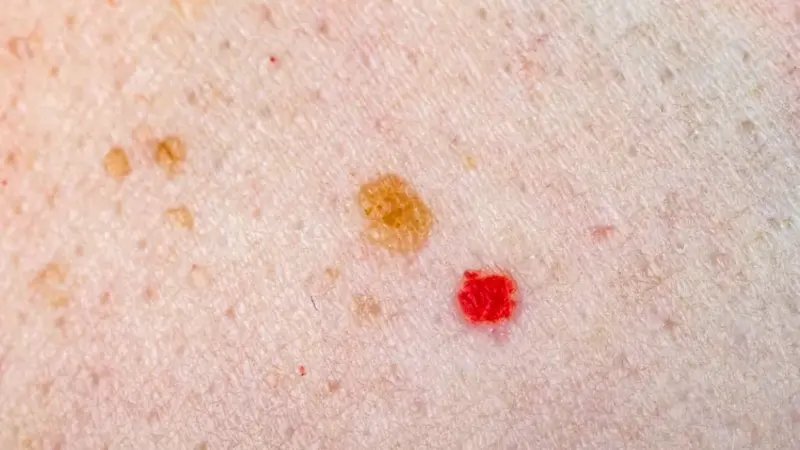
Cherry angiomas, also known as senile angiomas or Campbell de Morgan spots, are common, benign skin growths made up of small blood vessels. They typically appear on people aged 30 and older.
Symptoms
- Bright red, round, or oval spots: These are usually smooth and can vary in size.
- Typically found on the torso, arms, and shoulders: Though they can appear anywhere on the body.
Causes
- Aging: The exact cause is unknown, but they become more common with age.
- Genetics: There may be a hereditary component.
Treatment
- Usually not required: Cherry angiomas are benign and generally do not need treatment unless for cosmetic reasons.
- Laser removal: A laser can be used to remove the angiomas.
- Electrocauterization: This method involves burning the angiomas using an electric current.
Contact Dermatitis
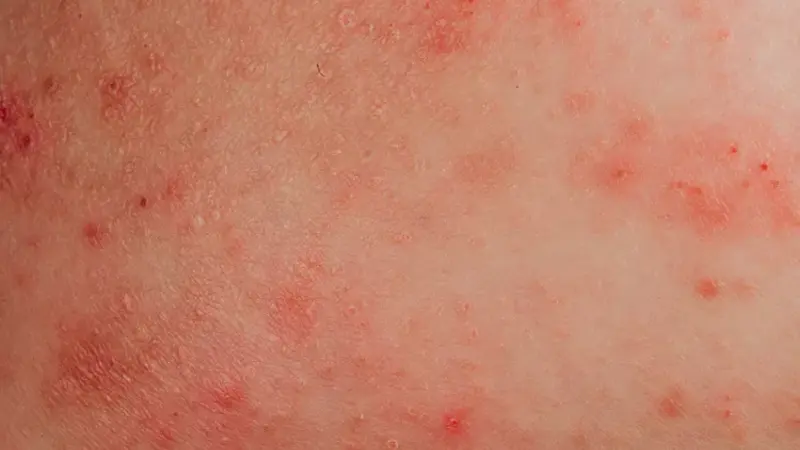
Contact dermatitis is an inflammatory skin condition caused by direct contact with an irritant or allergen. It is divided into two types: irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis.
Symptoms
- Red, itchy rash: The primary symptom of contact dermatitis.
- Dry, cracked, or scaly skin: In chronic cases, the skin may become very dry and flaky.
- Blisters: In severe cases, blisters may form and ooze.
Causes
- Irritants: Such as soaps, detergents, and solvents.
- Allergens: Such as nickel, poison ivy, and certain cosmetics.
Treatment
- Avoiding the irritant or allergen: The most effective way to prevent contact dermatitis.
- Topical steroids: Such as hydrocortisone cream, to reduce inflammation and itching.
- Moisturizers: To soothe and hydrate the skin.
Ringworm (Tinea Corporis)
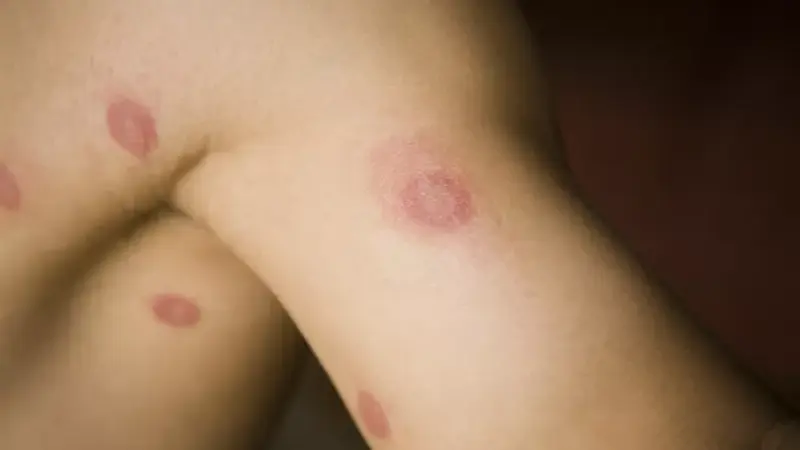
Ringworm, or tinea corporis, is a fungal infection characterized by a ring-shaped rash. Despite its name, it has nothing to do with worms.
Symptoms
- Red, circular, and scaly rash: Typically with raised edges and a clearer center.
- Itching: The rash can be itchy and uncomfortable.
- Blister-like lesions: In some cases, small blisters may form.
Causes
- Fungal infection: Caused by dermatophytes, a type of fungus.
- Direct contact: With an infected person, animal, or contaminated object.
Treatment
- Antifungal creams or ointments: Such as clotrimazole or miconazole.
- Oral antifungal medication: For severe or widespread infections.
Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema)
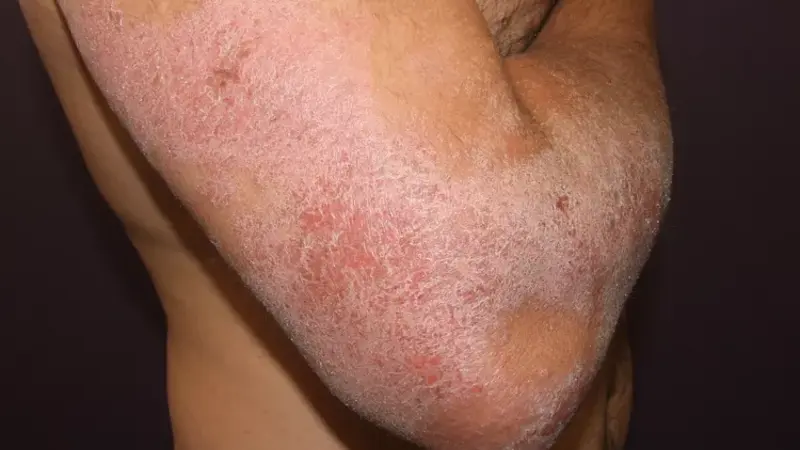
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic skin condition that results in red, itchy, and inflamed skin. It often starts in childhood and can be associated with other atopic conditions like asthma and hay fever.
Symptoms
- Dry, itchy skin: Often severe and persistent.
- Red to brownish-gray patches: Commonly found on the hands, feet, ankles, wrists, neck, upper chest, eyelids, and in the bends of the elbows and knees.
- Small, raised bumps: Which may leak fluid and crust over when scratched.
Causes
- Genetic factors: Eczema often runs in families.
- Environmental triggers: Such as allergens, irritants, and stress.
Treatment
- Moisturizers: To keep the skin hydrated.
- Topical corticosteroids: To reduce inflammation and itching.
- Avoiding triggers: Identifying and avoiding factors that can worsen the condition.
Drug Rash
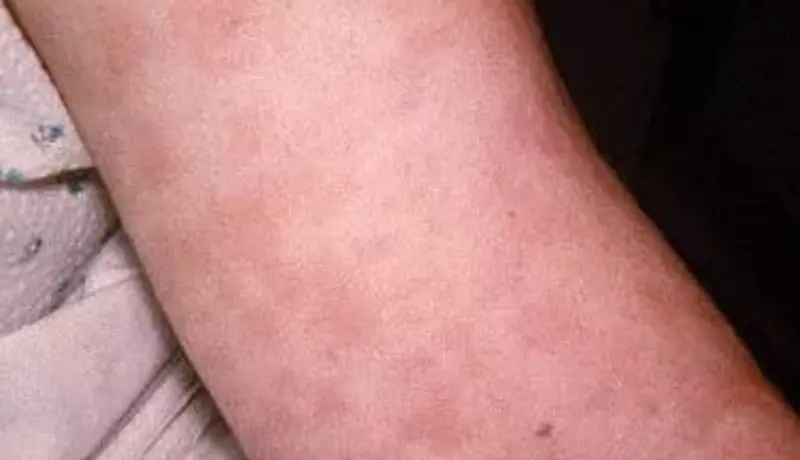
A drug rash is a skin reaction to a medication. It can range from mild to severe and can occur immediately after taking a drug or after prolonged use.
Symptoms
- Red, itchy rash: Often widespread and symmetrical.
- Hives: Raised, red, and itchy welts on the skin.
- Swelling: Especially of the face, lips, or tongue in severe cases.
Causes
- Medications: Such as antibiotics, anti-seizure drugs, and NSAIDs.
Treatment
- Discontinuing the offending medication: The first step in treatment.
- Antihistamines: To relieve itching.
- Corticosteroids: For severe reactions.
Pityriasis Rosea
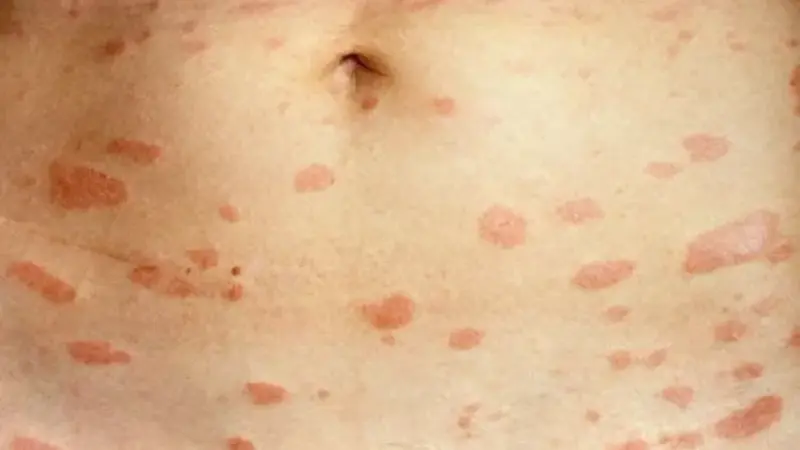
Pityriasis rosea is a common, self-limiting skin condition that typically starts with a single large patch known as the herald patch, followed by a rash of smaller spots.
Symptoms
- Herald patch: A large, oval, scaly patch that appears on the trunk.
- Secondary rash: Smaller patches that follow the lines of the skin in a Christmas tree pattern.
- Mild itching: Which can vary in intensity.
Causes
- Unknown: The exact cause is unclear, but it may be related to a viral infection.
Treatment
- Self-resolving: Pityriasis rosea usually goes away on its own within 6-8 weeks.
- Antihistamines: To reduce itching.
- Topical steroids: For severe itching.
Blood Spots (Purpura)
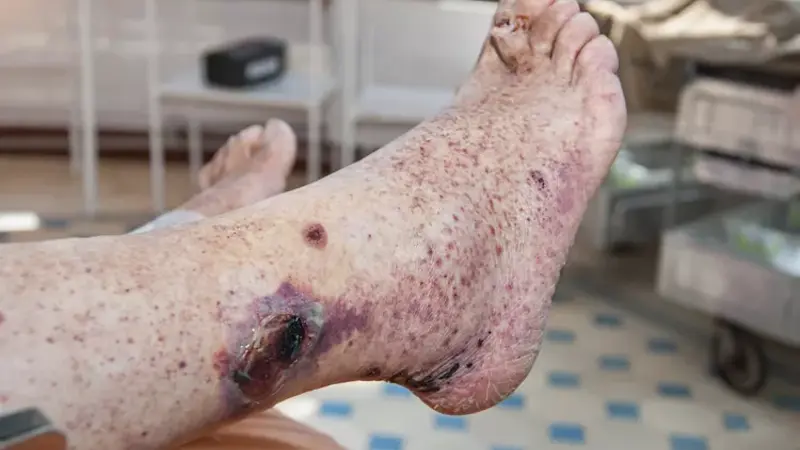
Purpura are red or purple spots on the skin caused by small blood vessels leaking blood under the skin. They can be a sign of various conditions.
Symptoms
- Red or purple spots: These do not blanch when pressed.
- Clustered appearance: They often appear in clusters.
Causes
- Bleeding disorders: Such as thrombocytopenia.
- Infections: Viral or bacterial infections.
- Medications: That affect blood clotting.
Treatment
- Addressing the underlying cause: Treating the primary condition causing purpura.
- Medical evaluation: Necessary to determine the severity and cause.
Swimmer’s Itch (Cercarial Dermatitis)
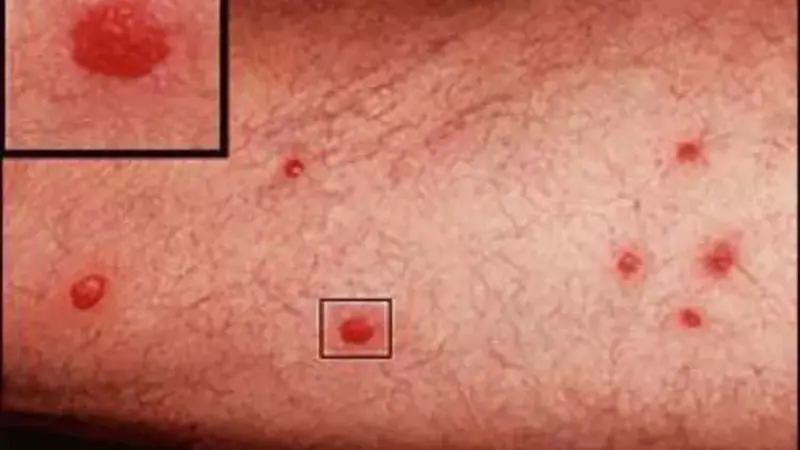
Swimmer’s itch, or cercarial dermatitis, is an allergic reaction to microscopic parasites found in contaminated water.
Symptoms
- Itchy, red rash: Appears shortly after swimming in infested water.
- Small blisters or pimples: The rash can develop into blisters.
Causes
- Parasites: The larvae of certain flatworms penetrate the skin.
Treatment
- Anti-itch lotions: Such as calamine lotion.
- Cool compresses: To reduce itching and inflammation.
- Avoiding contaminated water: Especially in areas known for swimmer’s itch.
Psoriasis
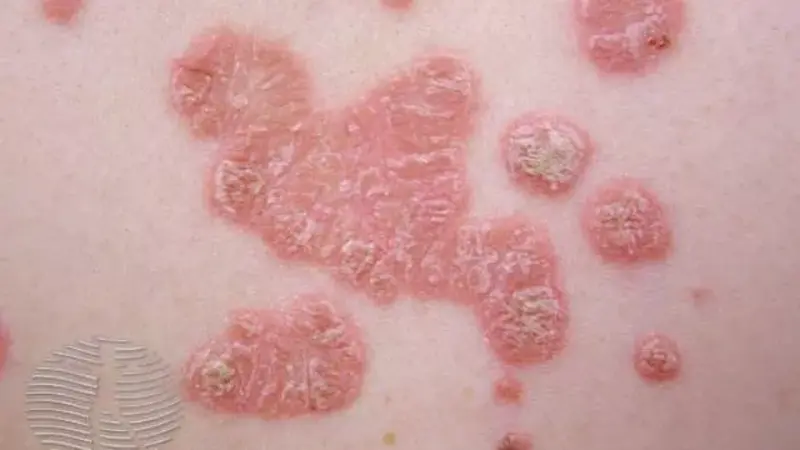
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that causes the rapid buildup of skin cells, leading to scaling on the skin’s surface. It is a long-lasting disease with no cure, but treatments can help manage symptoms.
Symptoms
- Red patches with silvery scales: Often found on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back.
- Dry, cracked skin: That may bleed.
- Itching and burning: In the affected areas.
Causes
- Immune system: Overactive immune response causes skin cell production to accelerate.
- Genetics: Family history can increase risk.
- Triggers: Such as infections, stress, and cold weather.
Treatment
- Topical treatments: Including corticosteroids, vitamin D analogues, and moisturizers.
- Light therapy: Using ultraviolet light.
- Systemic medications: For severe cases, such as biologics and oral medications.
Lichen Planus
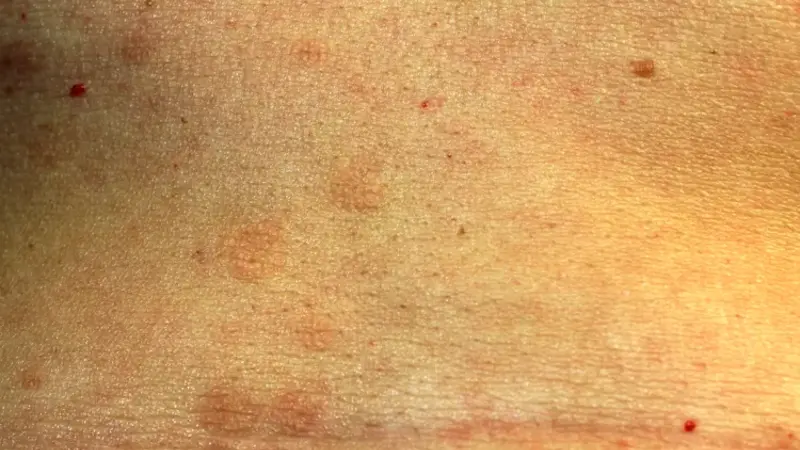
Lichen planus is an inflammatory condition that affects the skin and mucous membranes. It is characterized by purplish, flat-topped bumps and can cause long-term discomfort.
Symptoms
- Purple, flat-topped bumps: Often with a white, lacy pattern on the surface.
- Itching: Can be severe.
- Lacy white patches: In the mouth or other mucous membranes.
Causes
- Immune system: Believed to be an autoimmune reaction.
- Triggers: Such as hepatitis C infection and certain medications.
Treatment
- Topical corticosteroids: To reduce inflammation and itching.
- Antihistamines: For itching relief.
- Oral medications: For severe cases.
Petechiae
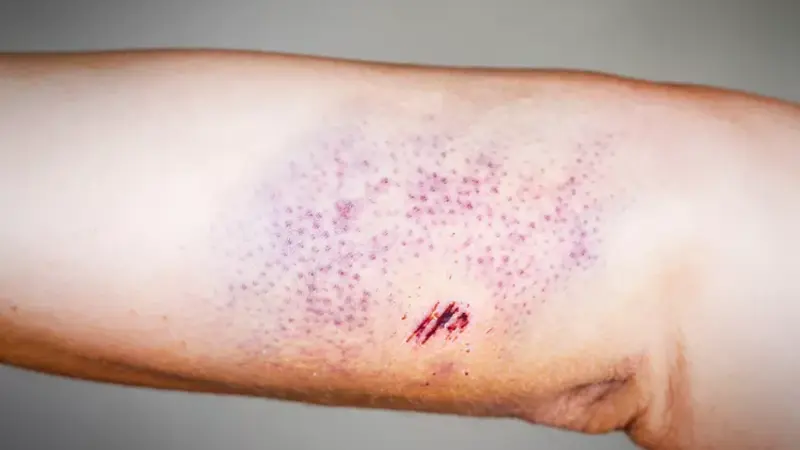
Petechiae are tiny, flat red or purple spots caused by bleeding under the skin. They can be a sign of a variety of conditions, from minor to serious.
Symptoms
- Small red or purple spots: About the size of a pinpoint.
- Clustered appearance: Often appearing in clusters.
- Non-blanching: The spots do not turn white when pressed.
Causes
- Infections: Such as viral or bacterial infections.
- Medications: That affect blood clotting.
- Bleeding disorders: Such as thrombocytopenia.
Treatment
- Addressing the underlying cause: Identifying and treating the primary condition.
- Medical evaluation: Necessary to determine the cause and severity.
Pimples (Acne Vulgaris)
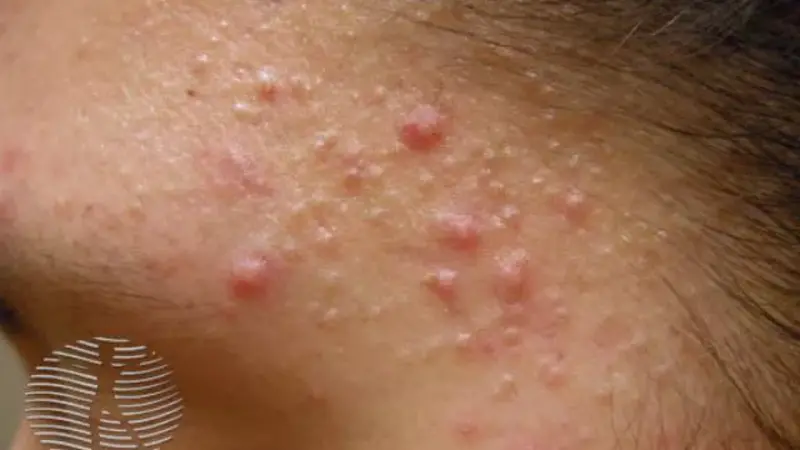
Acne vulgaris, commonly known as acne, is a skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells. It is most common in teenagers but can affect people of all ages.
Symptoms
- Whiteheads and blackheads: Closed and open comedones.
- Pimples: Red, inflamed bumps that can be painful.
- Nodules and cysts: Larger, deeper lumps that can cause scarring.
Causes
- Excess oil production: Sebum overproduction clogs hair follicles.
- Bacteria: Propionibacterium acnes can contribute to inflammation.
- Hormonal changes: Such as during puberty or pregnancy.
Treatment
- Topical treatments: Including benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, and retinoids.
- Oral medications: Such as antibiotics, hormonal treatments, and isotretinoin for severe cases.
- Proper skin care: Regular cleansing and avoiding pore-clogging products.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while red spots on the skin are often benign and self-limiting, they can sometimes indicate underlying health issues that require medical attention. By understanding the possible causes, symptoms, and treatment options for red spots on the skin, individuals can take appropriate steps to manage their condition and maintain skin health. If you have concerns about red spots on your skin, consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional for further evaluation and management.
Understanding these common skin conditions can help in identifying symptoms and seeking appropriate treatments. While many conditions can be managed with over-the-counter treatments, some require medical intervention. Always consult with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and treatment recommendations. Taking good care of your skin and addressing any concerns promptly can help maintain healthy and comfortable skin.If you have any questions, please visit the Kaz World Mag.